Tatooine-Like Binary Star Systems Could Be the Key to Finding Aliens

"Hearst Magazines and Yahoo may earn commission or revenue on some items through the links below."
We may need to widen our extra-terrestrial search to include binary and multi-star systems.
Astronomers have long sought signs of life in single-star systems much like our own.
The evolution of gas and dust in multi-star systems, according to research published earlier this month in the journal Nature, could serve as a catalyst for life.
We may be looking for aliens in all the wrong places.
Binary and multi-star systems, usually composed of two or more stars that either circle each other or a fixed point, may hold the key to finding extraterrestrial life, according to a new study from researchers at the University of Copenhagen in Denmark.
👽 You love science. So do we. We’ll help you make sense of it all—join Pop Mech Pro.
Astronomers have long targeted sun-like stars and their systems when searching the universe for life’s building blocks (the organic molecules that, when strung together, form amino acids and other proteins). After all, it’s the only type of system that we know contains life.
But observations in recent years have revealed that half of the star systems that contain sun-sized stars are actually binary systems. These places could be just as likely to house the ingredients for life, the researchers suggest.
Using Chile’s Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) telescope, the team observed NGC 1333-IRAS2A, a young binary star system 1,000 light-years from Earth. From that data, they developed a series of computer models that mapped out the system’s evolution both backward and forward in time. The goal was simple: explore how planets form in binary star systems.
“The observations allow us to zoom in on the stars and study how dust and gas move towards the disc,” Rajika L. Kuruwita, a post-d0c at the Niels Bohr Institute in Copenhagen, and one of the study’s authors, says in a prepared statement. “The simulations will tell us which physics are at play, and how the stars have evolved up till the snapshot we observe, and their future evolution.”
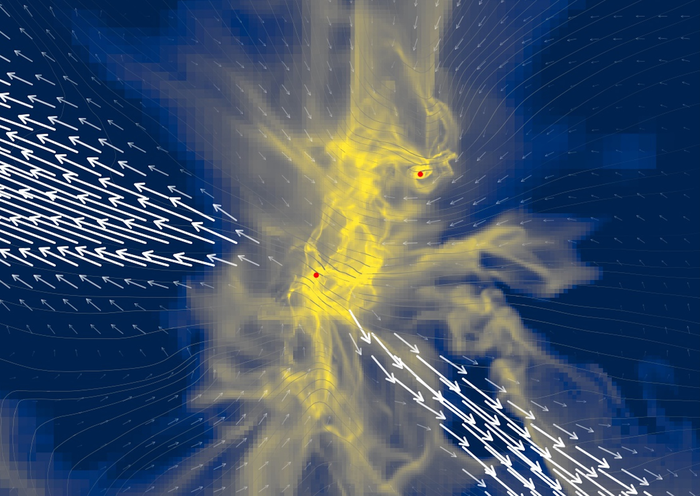
The models revealed that the protoplanetary disk—a churning mixture of gas and dust surrounding the twin stars—behaved in a peculiar way, speeding up and slowing down at different intervals. The team was able to model the disk’s movement in staggeringly granular detail and found that these change-ups in speed would occur roughly every few thousand years, sometimes taking place in as little as ten years.
This happens, the team hypothesized, because the gassy, dusty material is periodically sucked in by the stars’ massive gravitational pull. As material sped toward the stars, it caused them to heat up and subsequently grow brighter. This, in turn, can spur a cataclysmic jet of energy that tears apart the protoplanetary disk and dramatically alters the evolution of planets—and their molecular constituents—in the system. Kuruwita and her colleagues published the research last month in the journal Nature.
“This enhances the significance of understanding how planets are formed around different types of stars,” Jes Kristian Jørgensen, an astronomer also at the Niels Bohr Institute and one of the project’s leaders, says in the statement. “Such results may pinpoint places which would be especially interesting to probe for the existence of life.”
Next up, the team would like to schedule time on other telescopes—including the recently-launched James Webb Space Telescope (JWST); the forthcoming largest-optical-telescope-EVER, the European Large Telescope (ELT) in Chile; and South Africa and Australia’s Square Kilometer Array (SKA)—to observe the star system. These observatories will allow them to see the distant organic molecules (both trapped in ice and in gas form) in even finer detail.
You Might Also Like
