Lost for 105 Years at the Bottom of the Sea, Divers Have Finally Found the USS Jacob Jones
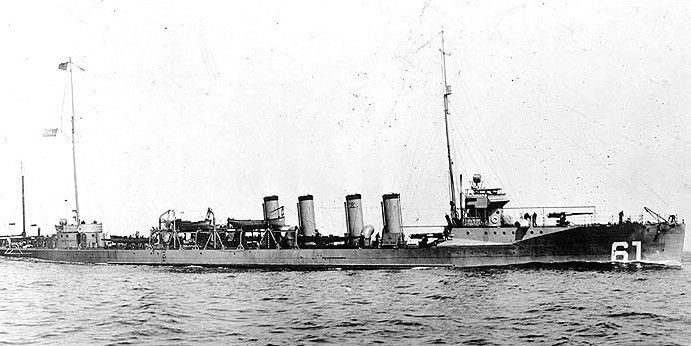
Divers have discovered the wreck of the U.S. Navy destroyer USS Jacob Jones.
The ship, sunk in 1917 by an enemy submarine, was the first American destroyer lost in combat.
The Navy has not lost a ship in combat since World War II, but it’s lost plenty to accidental sinkings, collisions, and fires.
The wreck of the first U.S. Navy destroyer sunk by enemy fire has been discovered. Divers from the British Sub-Aqua Club (BSAC) searching along the U.K. coastline discovered the remains of USS Jacob Jones, sunk by German U-boat torpedoes during World War I. Jacob Jones was an early example of the destroyer class, now the backbone of the modern Navy.
✈ Don’t miss any of our best-in-class military and defense news. Join our squad with Pop Mech Pro.
The wreck, according to Dive Magazine, was found approximately 40 miles off the Isles of Scilly archipelago, off the southwestern tip of the U.K., in 377 feet of water. The Darkstar team of explorers were acting off GPS data from the U.K. Hydrographic Office, which had recorded the location of unidentified wrecks.

Jacob Jones was a Tucker-class destroyer equipped with four 4-inch guns and eight 533mm torpedo tubes. Built for speed, Jacob Jones had two Curtis steam turbines, which delivered a total of 17,000 shaft horsepower, giving her a top speed of 30 knots. She was manned by a crew of 110 officers and other crew.
After America’s entry into World War I in 1917, Jacob Jones was assigned to convoy duty, bringing troops and supplies from North America to Europe. Although she did not sink any German U-boats, she did rescue hundreds of Allied merchantmen whose ships had been sunk by enemy submarines.
On the night of December 6, 1917, Jacob Jones was struck by a torpedo and sank, taking 64 of the crew members with her. Two of the crew members were captured by the submarine that sunk her, U-53, and the commander of the submarine radioed Allied forces the location of the remaining survivors, asking only that rescuers give him and his boat an hour to exit the area.
“No human remains were found or personal artifacts,” Dominic Robinson, BSAC’s head of diving and training, told Dive Magazine. “But for me, the thing that brought it home was the bent prop shaft—which shows the trauma the vessel must have been through when it was torpedoed. Absolutely incredible.”
Robinson’s team is coordinating with U.S. authorities on what to do next.

Destroyers were invented in the 1880s, when they were called torpedo boat destroyers. The fast little ships were meant to protect larger battleships and cruisers from the menace of even smaller, torpedo-armed boats. Eventually, with the advent of air power, “torpedo boat” was dropped from the name, and the ships became just “destroyers.” This signaled a shift in the mission of destroyers, away from fending off small boats to fending off two newer threats: submarines and airplanes.
The United States entered World War I in 1917, just a year before the armistice. By then, the war at sea had been largely won, and the United States lost just one armored cruiser, Jacob Jones, and a number of smaller transports and patrol craft. World War II was a far different story, with the Navy losing more than 70 destroyers between 1941 and 1945.
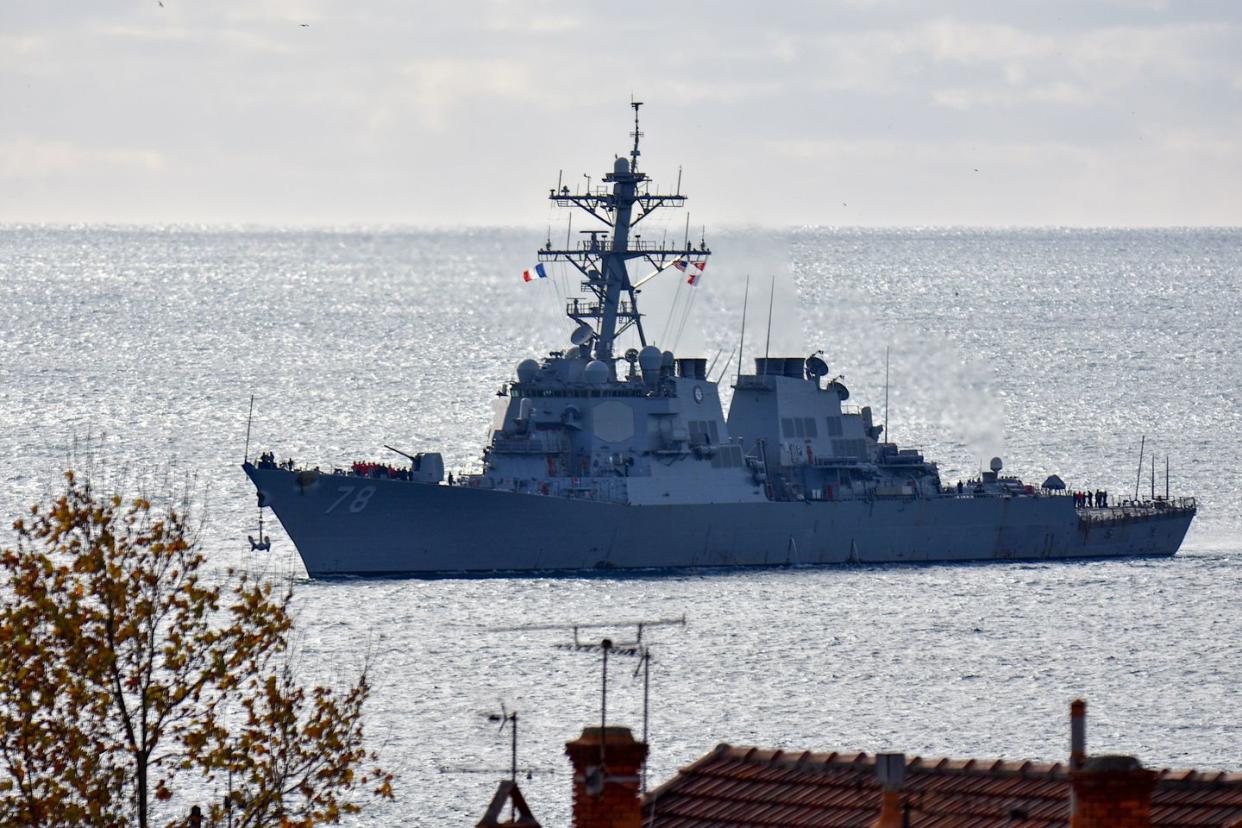

Destroyers have grown larger and more powerful over the past 100 years, transforming from the scrawny 1,000-ton “tin cans” of the World Wars to today’s 10,000-ton bruisers. The modern Arleigh Burke-class guided missile destroyers can engage everything from submarines to land targets hundreds of miles inland to satellites in low earth orbit. Destroyers have replaced battleships, the very ships they were invented to protect, as the backbone of the U.S. Navy surface fleet.
You Might Also Like
