Dominica country profile
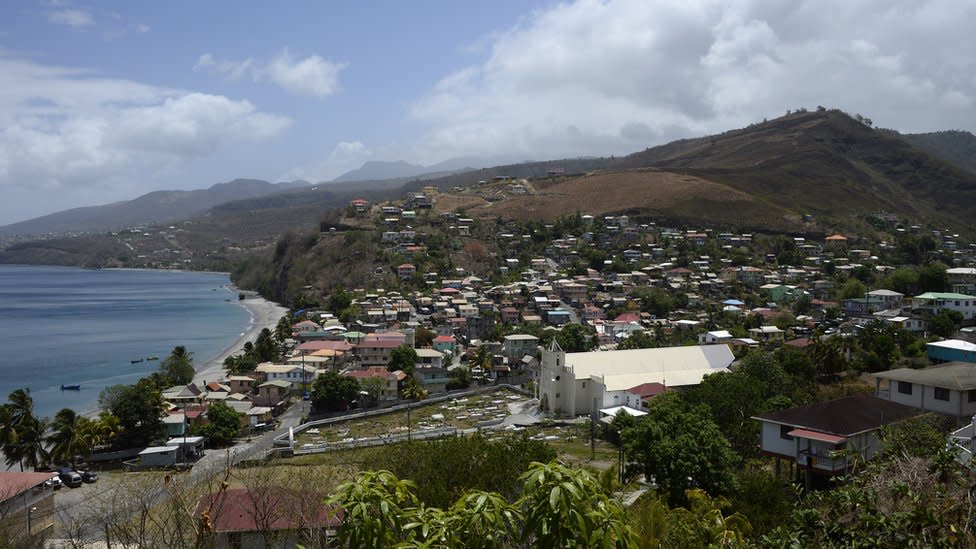
Dominica is a mountainous, forested Caribbean island nation with a year-round tropical climate, national parks, rare indigenous birds. and the second-largest boiling lake in the world.
It has significant tourism potential, but poor infrastructure and the absence of a large airport have impeded the industry's growth. The country is also vulnerable to hurricanes.
With few natural resources, Dominica is attempting to reduce its reliance on bananas, traditionally its main export earner.
The banana market has faced stiffer competition since the European Union was forced by the World Trade Organisation to phase out preferential treatment for producers from former colonies.
Read more country profiles - Profiles by BBC Monitoring
COMMONWEALTH OF DOMINICA: FACTS
Capital: Roseau
Area: 750 sq km
Population: 72,400
Languages: English, also Dominican Creole, Antillean Creole, French, Kokoy
Life expectancy: 71 years (men) 77 years (women)
LEADERS
President: Charles Savarin
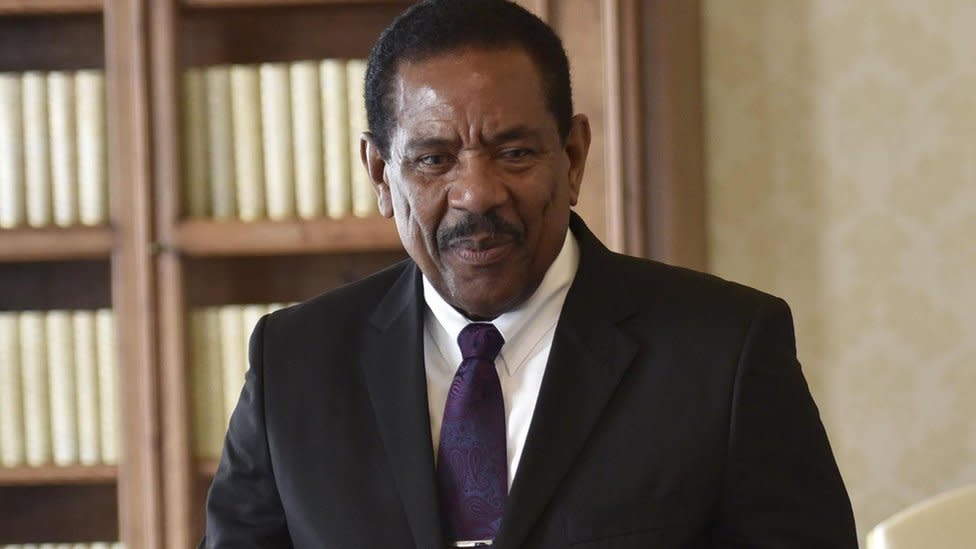

President Savarin, a former Labour Party cabinet minister, was appointed in September 2013, and re-elected in 2018.
Dominica's parliament, the House of Assembly, appoints the president - the ceremonial head of state. The prime minister and cabinet exercise executive power.
Prime minister: Roosevelt Skerrit
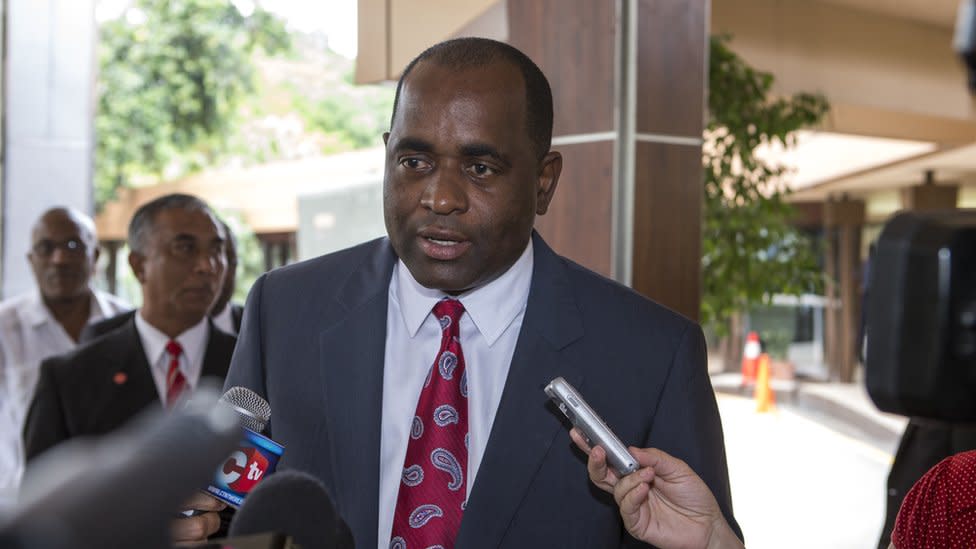

Roosevelt Skerrit's governing Dominica Labour Party won general elections in May 2005.
Campaigning on pledges to improve infrastructure and attract foreign investment, his government has won all subsequent elections - in December 2019, Skerrit won his fourth consecutive general election.
A former education minister, Mr Skerrit took office as Dominica's youngest prime minister two days after the sudden death of his predecessor Pierre Charles in 2004.
MEDIA

Dominica has a handful of weekly newspapers. There is no national terrestrial TV.
The radio scene includes public and private stations. Freedom House rates the media as "generally free".
Read full media profile
TIMELINE

Some key dates in Dominica's history:
1493 - Christopher Columbus visits the island and names it Dominica (Sunday Island).
1627 - English attempts at colonisation are fiercely resisted by the indigenous Carib community.
1635 - France claims Dominica, paving the way for French missionaries to colonise the island. However, resistance by the indigenous Carib Indians continues.
1660 - Britain and France agree to abandon Dominica and St Vincent.
1690 - French establish permanent settlements, following expeditions of English and French foresters, who have begun harvesting timber.
1763 - Britain gains possession of Dominica in accordance with the Treaty of Paris, which ended the Seven Years' War (1756-63). It establishes a legislative assembly, representing only the white population.
1782 - Battle of the Saintes: British defeat a French fleet off Dominica, ending a Spanish and French bid to invade Jamaica during the American Revolutionary War.
1831 - Britain confers political and social rights on free non-whites.
1834 - Slavery abolished.
1838 - Dominica becomes the first and only British colony in the Caribbean to have a black-controlled legislature.
1865 - Britain replaces the elected assembly with one consisting of one-half elected members and one-half appointed.
1896 - Britain re-establishes crown colony government over Dominica.
1951 - Britain declares universal adult suffrage.
1958-62 - Dominica becomes a member of the British-sponsored West Indies Federation.
1960 - Britain grants Dominica self-government, with a legislative council and a chief minister.
1978 - Dominica becomes independent.
1979 - Discontent with Prime Minister Patrick John's administration leads to a civilian coup and the formation of a caretaker administration under Oliver Seraphin.
1980 - Eugenia Charles becomes the Caribbean's first female prime minister.
1981 - Dominican Defence Force commander Frederick Newton leads a coup attempt in which a police officer is killed. The defence force is later disbanded as a result. Separately Canadian and US citizens, largely affiliated with white supremacist groups attempt to restore former prime minister Patrick John to power. John is initially tried and acquitted.
1985 - John is retried and found guilty. He is sentenced to 12 years imprisonment.
1986 - Former defence force leader and coup plotter Frederick Newton is executed.
1998 - Government announces plans to make Dominica a principal provider of offshore financial services "not only in the Caribbean, but the world".
2004 - Dominica cuts diplomatic relations with Taiwan in favour of ties with mainland China. China agrees to give aid worth more than $100m over five years.
2007 - Hurricane Dean wipes out 99% of Dominica's banana crop, putting further pressure on the island's struggling main industry.
2015 - Tropical Storm Erika devastates the island, killing 30 and causing severe environmental and economic damage.
2017 - Dominica is severely hit by Hurricane Maria, with up to 90% of buildings damaged and much of its infrastructure affected.

